The following examples present date
manipulation functions for different implementations, starting with Oracle. The
Employees table contains a date column named Hire_Date. All the examples in
this section retrieve a list of all employees who were hired in 2003.
SQL Statement :
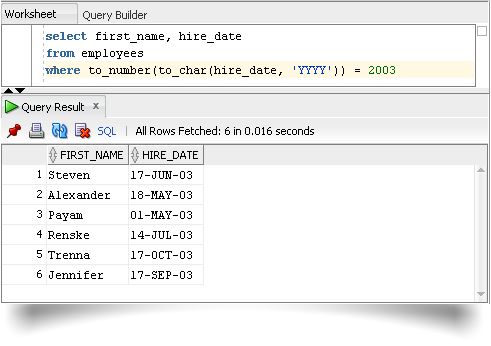
SELECT first_name,
hire_date
FROM employees
WHERE to_number(to_char(hire_date,
'YYYY')) = 2003;Output :
The table that follows describes how
you would issue the above statement in other DBMSs to get the same output using
platform specific date functions.
DBMS
|
SQL STATEMENT WITH SPECIFIC DATE FUNCTIONS
|
Alternate in Oracle using the BETWEEN operator
|
SELECT
first_name, hire_date
FROM
employees
WHERE
hire_date BETWEEN
to_date('01-JAN-2003') and to_date('31-DEC-2003');
|
Microsoft SQL Server
|
SELECT
first_name, hire_date
FROM
employees
WHERE
DATEPART(yy, hire_date) = 2003;
|
Microsoft Access
|
SELECT
first_name, hire_date
FROM
employees
WHERE
DATEPART('yyyy', hire_date) =
2003;
|
MariaDB and MySQL
|
SELECT first_name, hire_date
FROM employees
WHERE
YEAR(hire_date) = 2003;
|
SQLite
|
SELECT
first_name, hire_date
FROM
employees
WHERE
strftime('%Y', hire_date) = 2003;
|
PostgreSQL
|
SELECT
first_name, hire_date
FROM
employees
WHERE
DATE_PART('year', hire_date) =
2003;
|
There is a long list of such
functions for each platform. Refer to your DBMS documentation for the list of
the date-time manipulation functions it supports. Since we’re connected to an
Oracle database session, we’ll explore some date functions specific to Oracle
in the next few sections.
No comments:
Post a Comment