In many situations you search for records in
your database whose exact values are unknown. Using the LIKE operator along
with a character pattern (search string) you can easily find the match. The
character pattern is constructed with the help of two special characters: % and
_. The percent character (%) represents zero or more characters, while the
underscore character (_) represents just one. The first example below searches
all employees starting with the letter ‘A’. The second statement displays a
list of all employees who do not contain ‘a’ within their names. The third
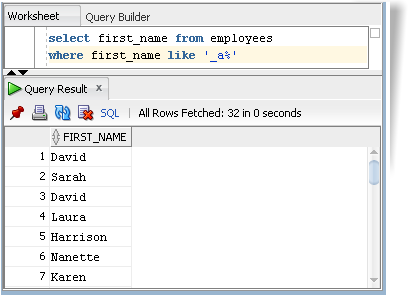
example searches for employees whose first name has an ‘a’ as the second
letter.
SQL Statement :
Output :
SQL Statement :
SQL Statement :
Output :
NOTE
Some
DBMS are case sensitive, therefore you must take care of it while using the
LIKE operator. For example, such DBMS would treat 'adam' and 'Adam'
differently. Microsoft
Access uses * instead of % and ?
instead of _.
SQL Statement :
SELECT first_name
FROM employees
WHERE first_name LIKE ‘A%’;Output :
SQL Statement :
SELECT first_name
FROM employees
WHERE first_name NOT LIKE ‘%a%’;
Output :
SELECT first_name
FROM employees
WHERE first_name LIKE ‘_a%’;Output :


No comments:
Post a Comment